top of page
T
Tinea
Etiology: dermatophytes
Location/Appearance/Tx:
-
Tinea corporis = body
-
annular, scaly, erythematous plaques with slightly raised borders and partial central clearing
-
topical antifungals (terbinafine)
-
-
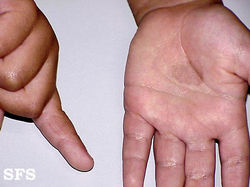
Tinea manuum = hand
-
fine palmar scaling + dryness with redness
-
topical antifungals (terbinafine)
-
-
Tinea cruris = groin
-
well demarcated scaly borders
-
topical antifungals (terbinafine) + absorbant powders + loose undergarments
-
-
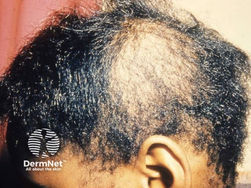
Tinea capitis = scalp
-
broken hairs resembling dots, a moth eaten appearance due to patchy hair loss
-
oral griseofulvin
-
-
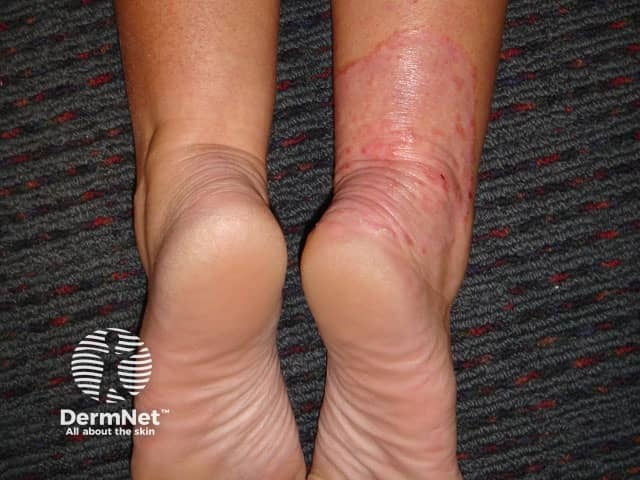
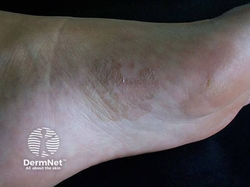
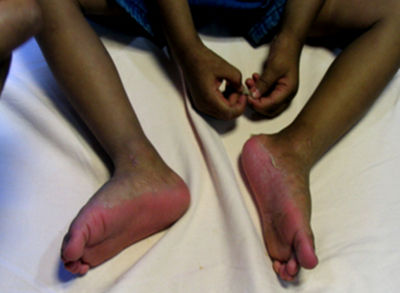
Tinea pedis = foot
-
silvery white scaling along soles or plantar surface
-
topical antifungals (terbinafine) + powders
-
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Etiology: S. aureus enterotoxin Type B or toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1) from tampons or other foreign objects located in the body for a long period of time
Sx:
-
fever, diffuse macular erythematous rash, low BP
-
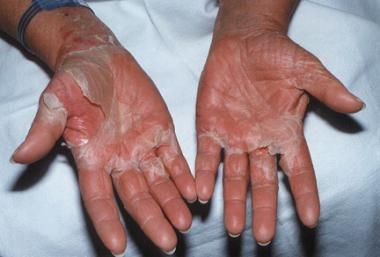
shedding of the skin in large sheets, especially from palms + soles, 1-2 weeks after the onset of illness
Location: palms + soles
Tx: supportive care + systemic abx
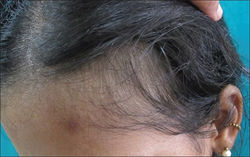
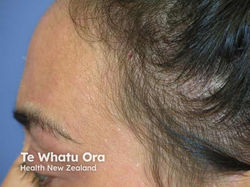
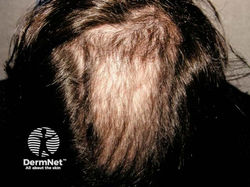
Traction Alopecia
Location: frontal hairline, sides
Etiology: regularly wearing tight chignon, cornrows, dreadlocks, weaves, braids, hair extensions, and chemical relaxers and rollers
Description: itching, redness, scaling, folliculitis, multiple short broken hairs, hair loss
At risk: African American women
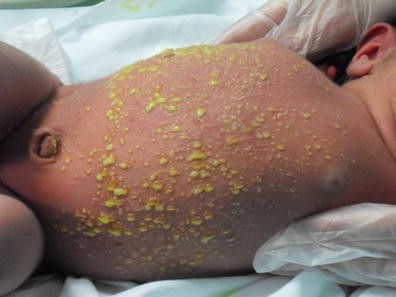
Transient Neonatal Pusular Melanosis
Etiology:
Appearance: pustules that rupture leaving scale and PIH
At risk: skin of color



1/4
Trichostasis Spinulosa
Etiology:










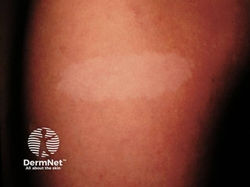
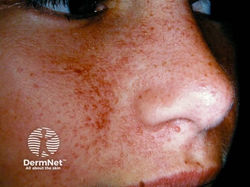
Tuberous Sclerosis
Etiology: mutation in TSC1 (hamartin), TSC2 (tuberin)
Inheritance: AD
Description: hypomelanotic macules / ash-leaf spots + angiofibroma (small bumps especially around nose + cheeks)
bottom of page