top of page
D
Darier Disease / Keratosis Follicularis
Etiology: mutation of ATP2A2 gene
Inheritance: AD
Appearance: scaly crusted papules and greasy plaque; alternating red + white nail beds with V-shaped nicking
Location: seborrheic dermatitis distribution (oily areas of the body like chest, back, scalp margins, forehead, nasolabial folds, eyebrows, beard) and skin folds
At risk: adolescents
Tx: moisturizers, topical retinoids, sun protection
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |
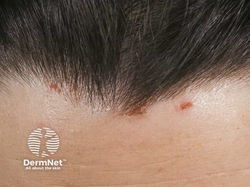
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Etiology: cross-reactivity between anti-gliadin IgA antibodies + transglutaminase at the dermal basement membrane
Appearance: papulovesicles or excoriated papules on erythematous base
Location: elbows, dorsal forearms, knees, scalp, buttocks
Sx: intense itching
At risk: pts with Celiac Disease, Irish or Swedish patients
Associated with: maltomas
Tx: gluten free diet, dapsone
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
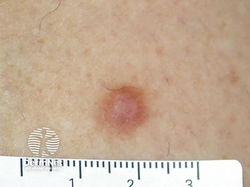
Dermatofibroma
Etiology: trauma (mosquito bite, shaving nick)
Appearance: tan to pink, firm, hyperpigmented dome-shaped papules with peripheral rim of darkening pigment
Location: extremities
Prog: once you get one, you're at risk of getting more
Dermoscopy: peripheral fine network, central white or pink scar-like area, ring-like globules, dotted vessels
At risk: adults
Test: "dimple or pinch" sign
Tx: reassurance
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Etiology: rare type of skin cancer characterized by its slow-growing, locally aggressive nature; unknown cause, but an injury is a predisposing factor
Appearance: skin colored, pink or brown irregular border multi nodular fungating mass
Histo: storiform spindle cells very deep with fat getting trapped in it
Sx: painless plaque +/- nodules that feels rubbery or firm to touch
At risk: adults between 20- 60 yo
Location: trunk
Tx: MOHs favored over wide excision; imatinib if t17;22










Dermatographia
Etiology: skin trauma may release an antigen that reacts with the membrane bound IgE on mast cells triggering histamine release
Appearance: linear wheals + a surrounding erythematous flare which appears 1-3 minutes after stroking + resolves in 30-60 minutes
At risk: young adults
Tx: loose fitting clothes, avoid triggers, antihistamines, phototherapy, omalizumab




1/7
Dermatomyositis
Etiology: unknown; classic model considers DM to be the result of a humoral attack against the endothelium of muscle capillaries + small arterioles; risk factors include underlying malignancy + family hx of autoimmune disease
At risk: 30-50 yo, females
Sx: rash appears weeks to months before proximal muscle weakness
Locations:
-
extensor surfaces of MCP + IP = Gottron papules
-
upper eyelids = Heliotrope
-
malar-like rash
-
chest = V neck sign = Poikiloderma
-
upper back = Shawl sign
-
lateral thigh = Holster sign
Ass. conditions: adenocarcinomas
Tx: systemic CS
Dermatophytosis / Tinea / Ringworm
Etiology: Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum
Appearance: annular erythematous plaque with central clearing and raised scaly edge
Sx: itchiness
Locations:
-
tinea barbae = beard
-
tinea capitis = head
-
tinea corporas = body
-
tinea cruris = groin
-
tinia unguium = nails
-
tinea pedis = foot
At risk: hot humid climates
Tx: topical antifungals (imidazole, terbinafine) unless if it is on head or nails (oral instead: itraconazole, itraconazole)
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra
Etiology: activating mutation in FGFR3
Appearance: 1-5 mm in diameter, hyperpigmented brown-black sessile to filiform, smooth surfaced papules
Location: cheeks, temples
At risk: Fitzpatrick types 4/5/6, females
Tx: EDC (for darker skin), cryo (for lighter skin), Nd:YAG laser




1/10
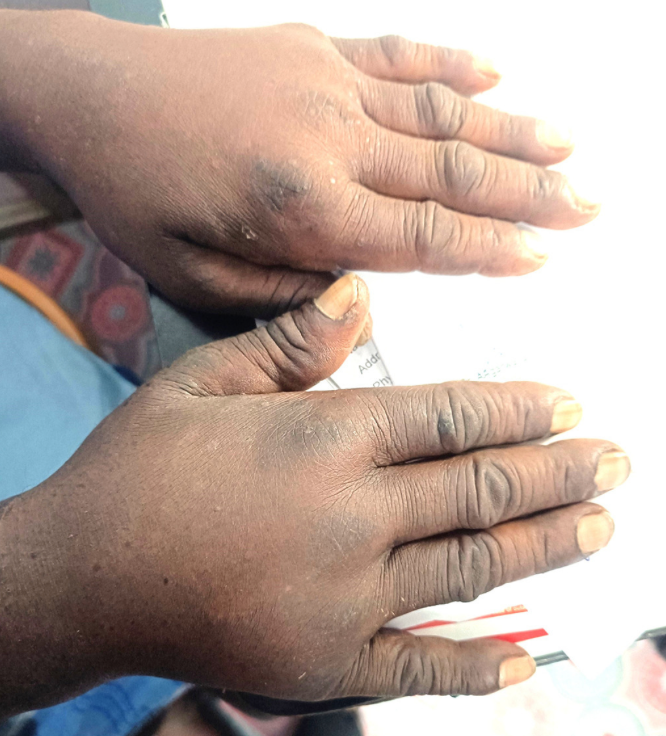
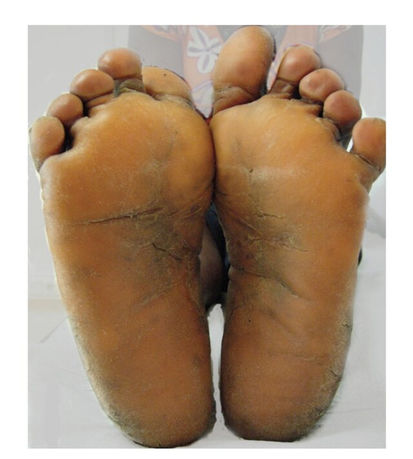
Diffuse Palmoplantar Keratoderma (DPK)
Etiology: genetic abnormality
Inheritance: AR or AD
Appearance: hyperkeratosis with white/yellow hue
Sx: hyperhidrosis
Location: symmetric palmar + plantar surfaces
Tx: emollients, keratolytic agents (salicylic acid, propylene glycol), topical retinoids, oral retinoids (acitretin), topical vitamin D (calcipotriol)
Etiology: mutation in: MVD, MVK, FDPS, PMVK or SART3 genes; results in decreased cholesterol in the affected areas of the skin
Inheritance: AD
At risk: European, females
Locations: arms, legs
Appearance: irregular annular plaque with elevated horny rim
Prog: <10% turn into SCC
Tx: compounded off-label topical 2% lovastatin +/- topical cholesterol, sun protection education
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
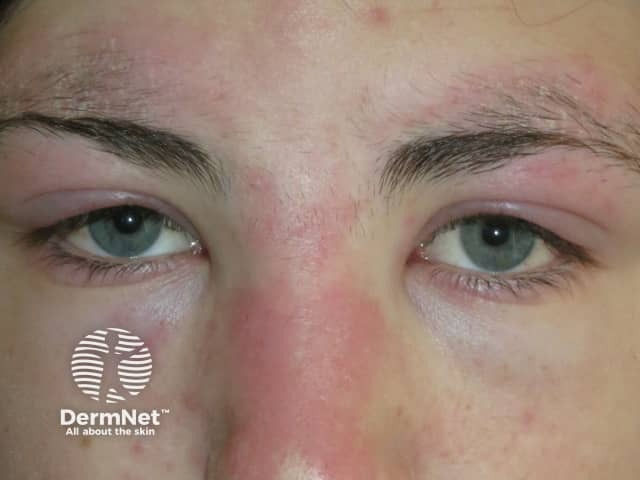
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Etiology: delayed type IV HS reaction to certain medication (anti epileptics, allopurinol, sulfonamides, minocycline, HIV meds)
Appearance: facial edema, diffuse erythematous macules + plaques that typically occur in 3rd week after starting a med or increasing dose
Ass. sx: high fever, lymphadenopathy, hematological abnormalities, hepatitis, nephritis, carditis, other organ involvement, facial swelling
Location: first involves face, upper trunk, UE, and then spreads to LE
Tx: stop all suspect medications, systemic CCS, cyclosporin, IVIG
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |
Dyskeratosis Congenita (DC)
Etiology: 14 different genes (DKC1 gene mutations on X chromosome); causing telomere shortening = premature aging
Inheritance: AD or AR
Appearance: lacy reticular hyperpigmentation
Other sx: nail dystrophy, oral leukoplakia, early hair greying, sparse eyelashes, hyderhidrosis
Location: upper chest, neck, nail atrophy, oral leukoplakia
Tx: no cure; tx is aimed at maintaining bone marrow function via oxymetholone as this is the major cause of death
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
bottom of page