top of page
E
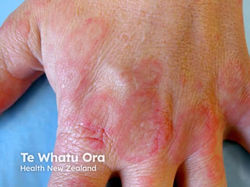
Ecthyma
Etiology: deep erosion of impetigo into the dermis via S. aureus + S. pyogenes
Appearance: begins as a vesicle or pustule on inflamed skin, then develops a hard crust covering the blister; if crust is removed, lesion will reveal an ulcer that is erythematous, edematous, and oozing pus
Location: buttocks, thighs, legs, ankle, feet
At risk: immunocompromised, warmer climates
Tx: topical antibiotics (fusidic acid, mupirocin) oral abx (dicloxacillin or flucloxacillin are go-to's)
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |
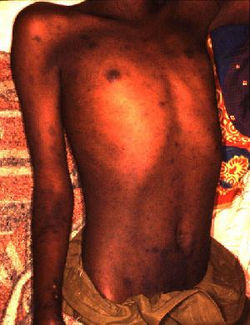
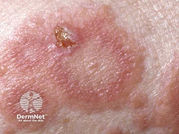
Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Etiology: P. aeruginosa
Appearance:
-
painless, annular, erythematous patches that rapidly become pustular
-
hemorrhagic focus appears in the center + forms a blister that spreads peripherally
-
gangrenous ulceration develops with a black/gray scab surrounded by a red halo
At risk: immunocompromised, critically ill
Tx: piperacillin, FQ, aminoglycosides
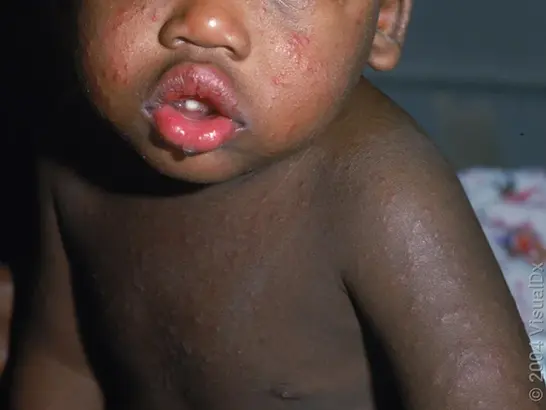
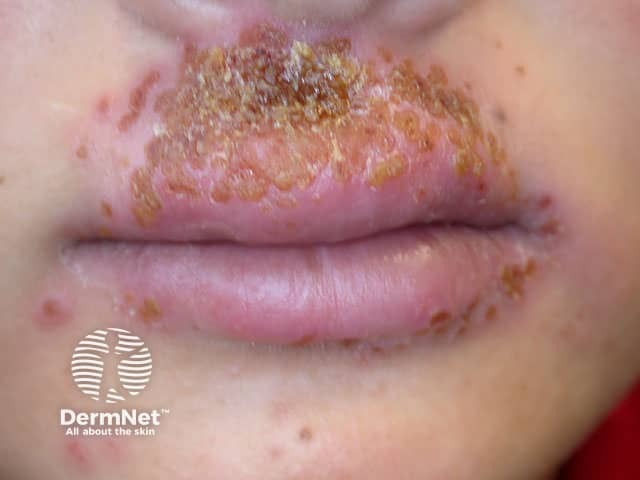
Eczema Herpeticum
Etiology: HSV 1 or 2 infection
Appearance: clusters of erythematous based vesicles that spread over 7–10 days + may rarely be widely disseminate
Sx: fever, and itchy vesicles
At risk: infants + children with atopic dermatitis
Location: face + neck
Tx: oral acyclovir







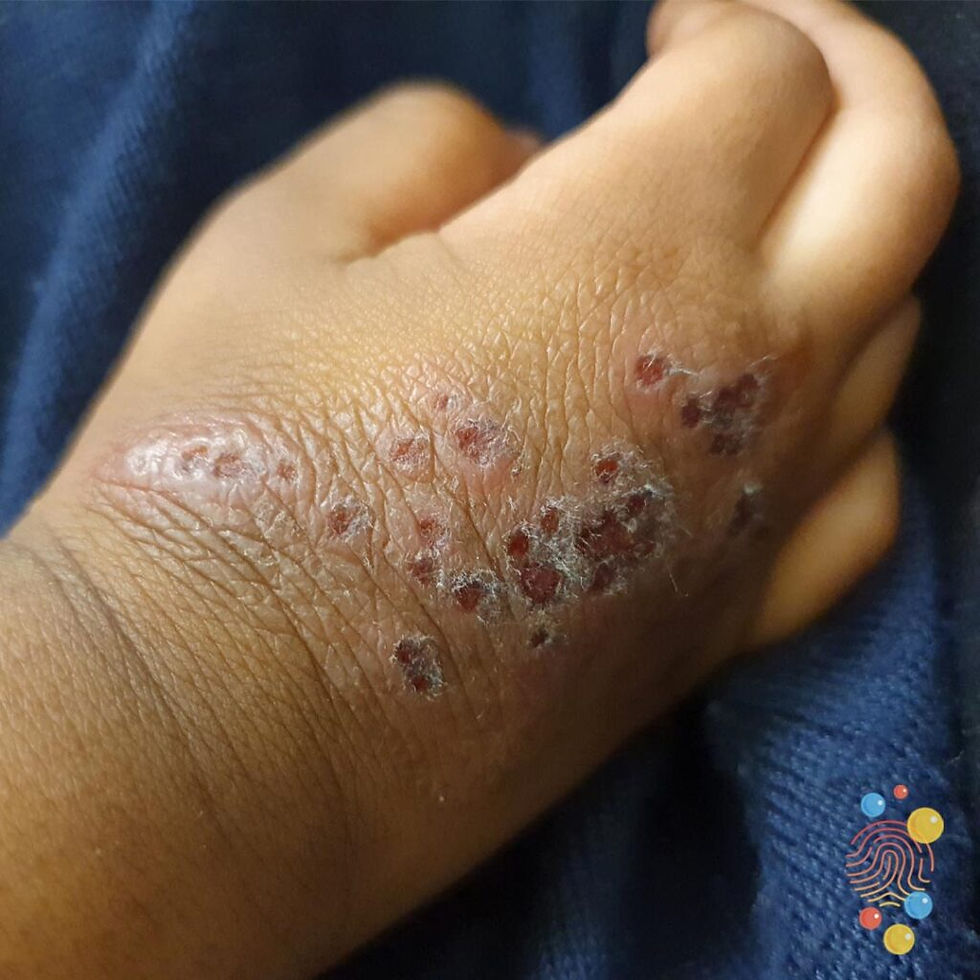















Epidermolysis Bullosa
Etiology: gene mutation (KRT5, KRT14, LAMA3, LAMB3, COL7A1) that makes the skin more fragile
Inheritance: AD or AR (multiple subtypes)
Appearance: blisters which burst easily and leave slow-healing wounds
Location: sites of friction and minor trauma (hands + feet)
Types:
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa
- Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- Kindler syndrome
Tx: gene therapy + cell based therapy; treat symptoms (protect skin, stop blisters, promote healing, prevent complications)






















Erysipelas
Etiology: S. pyogenes that infects the upper dermis
Location: lower extremities > face
Sx: systemic symptoms before onset of well demarcated erythematous plaque with burning, tenderness, and itching
Ass. sx: fevers, chills, shivering
At risk: immunocompromised, DM, very young + very old
Tx: oral penicillin
Erythema Induratum of Bazin
Etiology: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Appearance: erythematous to violaceous nodules or plaques that can ulcerate and scar
Sx: tender, painful
Location: posterior lower leg
At risk: young to middle-aged women
Tx: slow resolution over months; compression therapy, leg elevation, and NSAIDs



1/3
Erythema Infectiosum / Fifth Disease / Slapped Cheek Rash
Etiology: Parvovirus B19
Appearance: classic malar rash beginning 2-5 days after onset of other sx; few days later a lacy race appears on trunk + extremities
Other sx: HA, mild fever
Transmission: respiratory secretions
At risk: children + daycare workers
Tx: self limited
Preventative: Affected children may remain at school, as the infectious stage or viremia occurs before the rash is evident
Erythema Multiforme
Etiology: HSV (MC), TB, mycoplasma pneumonia, other chemicals or medications
Appearance: targetoid lesion - central dusky purpura with an elevated edematous pale ring; typically occurring 1-2 weeks after infection
Location: extremities and spreads centripetally
Sx: painful
At risk: 20-40 yo, males, genetic predisposition for HLA-DQB1* 0301 allele
Tx: self limited; topical CS can relieve symptoms
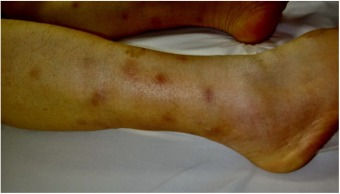
Erythema Nodosum
Etiology: delayed type IV HS reaction that can be triggered by infection, drugs, inflammatory disease, Hodgkin lymphoma, sarcoidosis, pregnancy
Appearance: erythematous, immobile nodules
Sx: tender nodules, fever, joint pain, edematous ankles
Location: anterior lower legs
At risk: women, 25-40 yo
Tx: self limited, treat underlying condition, bedrest, leg elevation, compression stockings
Prog: resolve within a month
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
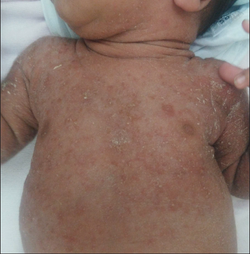
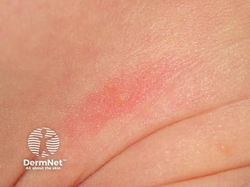
Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum (ETN)
Description: erythematous macules, papules, and pustules that can erupt over several days and it is unusual for an individual lesion to persist for more than a day; appears in the first 4 days of life
Histo: predominantly eos
Location: starts on face, spreads to trunk and limbs; spares palms + soles
At risk: newborns
Tx: reassurance
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |
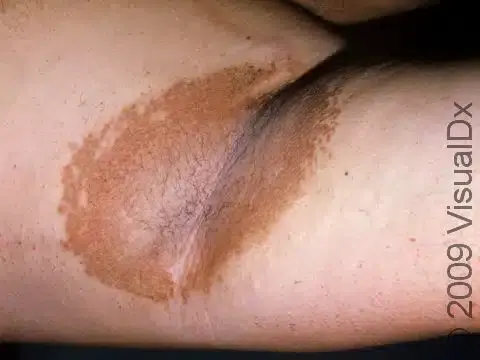
Erythrasma
Etiology: Corynebacterium minutissimum
Appearance: well defined pink to brown patches with fine scale and superficial fissures
Location: folds under arms, groin (males), between toes (females)
At risk: humid environment, sweating, obesity, poor hygiene
Tx: fusidic cream, clindamycin solution, benzoyl peroxide, Whitfield ointment











Erythroderma
Etiology: drugs, AD, psoriasis, PRP, GVHD, internal malignancies, CTCL
Appearance: generalized erythema with scales covering >80% of BSA
Sx: fevers, chills, pruritus, peripheral edema
At risk: males
Tx: discontinue all unnecessary meds, monitor fluid balance and body temp, keep skin moisturized, treat underlying cause
Exanthematous Drug Eruption
Appearance: erythematous macules and papules
Location: first appear on trunk and spread centrifugally to extremities in symmetric fashion
Timing: 7-10 days after drug initiation or 24-48 hours after repeat drug initiation
Sx: fever, pruritus
Tx: topical steroids, oral antihistamines
Prog: resolves in a few days to a week after med stopped
Extramammary Paget Disease
Etiology: intraepithelial adenocarcinoma
Appearance: asymmetrical, erythematous to pink plaque with ulcer and overlying crust
Sx: pruritus, burning, pain
Location: vulva (females), perianal (men)
At risk: 50+ yo, Caucasians
Tx: wide local excision and MOHs




1/4
bottom of page