M
Mal de Meleda
Appearance: glove + stocking malodorous keratoderma, more erythematous
Inheritance: AR
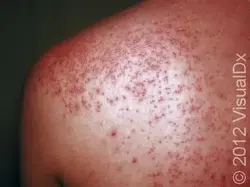
Mastocytosis
Etiology: Gain of function mutation in KIT gene = growth of mast cells = more histamine release
Description: small reddish-brown spots or bumps (urticaria pigmentosa)
Darier sign
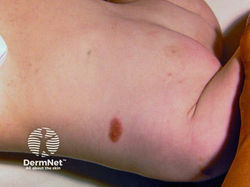
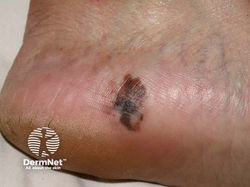
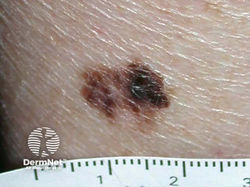
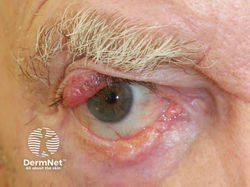
Melanoma
Etiology: BRAF, NRAS, c-KIT, GNAQ, GNA11, CDKN2A, MC1R mutations; UV light exposure
Appearance: irregularly pigmented, asymmetrical macules or papules (ABCDE)
Types:
-
superficial spreading
-
nodular
-
lentigo maligna
-
acral lentiginous
Dermoscopy: blue/white veil, dark globules, peripheral globules, negative pigment network, pseudopods, radial streaming
Tx: wide local excision
Screening post dx:
-
q3 mo for 1st yr
-
q6 mo <5 yrs
-
q1 yr >5 yrs
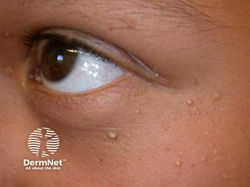
Milia
Appearance: 1-2 mm white to yellow subepidermal papules
Location: cheeks, eyelids, forehead, genitalia
Tx: nick surface + express; tretinoin
Cause: small cyst containing keratin
Description: tiny pearly-white bumps just under the surface of the skin
Locations: face, especially eyelids + cheeks
 single milium |  common on cheeks |
|---|---|
 Eruptive milia |  Milia en plaque |
 Childhood milia |  Milia en plaque |
 Following injury |  |
 Following bullous pemphigoid | 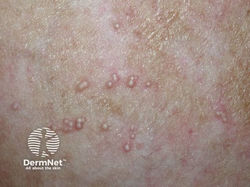 Following bullous pemphigoid |
 |  |
 |  Neonatal milia |
 |
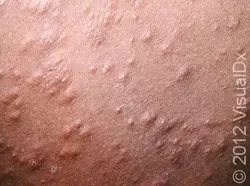
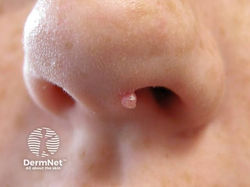
Molluscum contagiosum
Etiology: poxvirus
Appearance: flesh colored dome-shaped papules +/- umbilication
Location: anywhere, but palms + soles are typically spared
Transmission: skin to skin + skin to fomite
Tx: self limited or if tx is wanted (cryo, cantharidin, podophyllotoxin cream)
BOTE sign = "Beginning Of The End" = indicates lesion is resolving due to the body's immune response; characterized by redness, tenderness + crusting
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
Mpox / Monkeypox
Etiology: Orthopoxvirus
Description:
1. first 5 days of the infection, patients experience 'flu-like' symptoms
2. rash similar to that seen in chickenpox develops
3. maculopapules,evolve into vesicles, pseudpustules, crusting over, andn atrophic scars and lasts for around 10 days
Location: Lesions predominate on the face but may develop on the palms, soles, and dorsal hands and feet
At risk: MSM, endemic to Africa
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Mycosis Fungoides
Etiology: unknown; triggers proliferation of cerebriform T cells
Description:
-
Patch stage = flat erythematous scaling with well-defined borders in non-sun-exposed areas or hypopigmented lesions on darker skinned individuals
-
Plaque stage = pruritic raised borders with irregular contours and reddish-brown in color
-
Tumor stage = exophytic violaceous lesion
 Patch stage MY PUBLICATION :) |  Plaque stage |
|---|---|
 Patch stage |  Patch stage |
 Patch stage |  Plaque stage |
 Plaque stage |  Plaque stage |
 Patch & Plaque stage |  Tumour stage |
 Tumour stage |  Tumour stage |
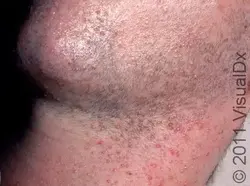
Myofibroma
Histo: hypocellular pink blue nodules with dilated branching staghorn vessels and cellular areas
At risk: babies/kids
Types:
-
Single – MC, skin/SQ nodule
-
Muliptle
-
Generalized