H
Hand Foot & Mouth Disease
Etiology: Coxsackie A
Description: vesicular rash
Location: around the lips, mouth, and back of the throat
Hand-Foot Syndrome
Etiology: chemotherapy agents (5-FU, capecitabine)
Description: sunburnt-like hands that appears 2-3 months after starting chemotherapy where the whole sole or palm turns completely red




Hand-Schüller-Christian Disease
Etiology: unknown cause, but the number of Langerhans cells in the skin and other organs are triggered to increase (type of Langerhans cell histiocytosis); BRAF V600E mutation associated
Description: Pinkish crusted papules with lytic bone lesions in skull, diabetes insipidus, and exophthalmos
At risk: 2-6 yo



Harlequin Ichthyosis
Define: severe genetic skin disorder characterized by thick, diamond-shaped plates of skin separated by deep cracks
Tx: oral retinoids
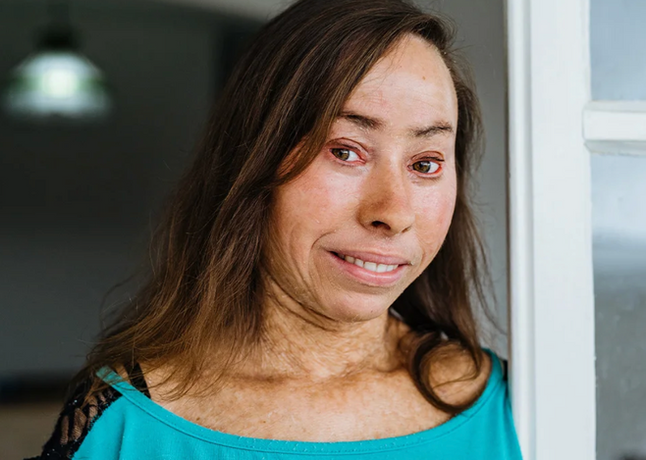
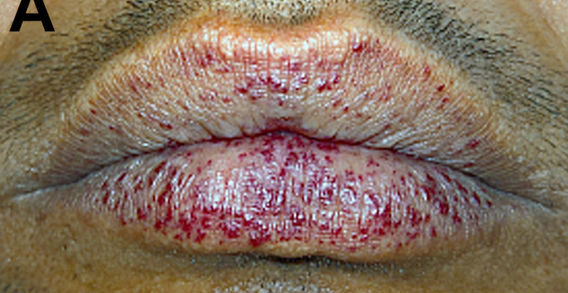
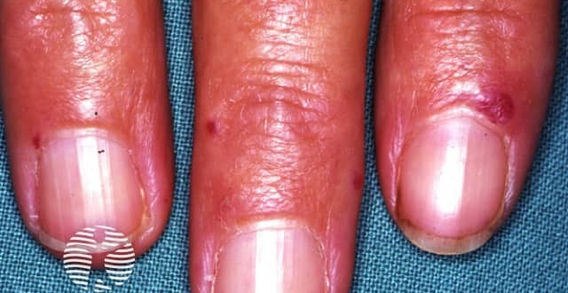
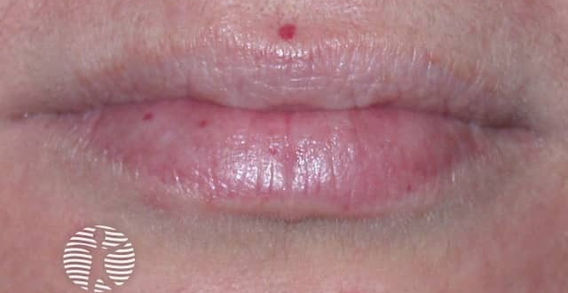
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia / Osler-Weber-Rendu
Etiology: AD mutation (loss of function of ENG gene) causing thin-walled blood vessels, especially in the mouth and GI tract
Description: blanching lesions (telangiectasias) on skin and mucous membranes, recurrent epistaxis, skin discolorations, arteriovenous malformations, GI bleeding, hematuria
Herpes Labialis (cold sores)
Etiology: HSV1
Description: shallow oral ulcers that rupture and dry after a few days forming a thin, yellowish crust and will completely heal
At risk: children (transmitted through contact with oral secretions)
Herpes Zoster / Shingles
Etiology: recurrent VZV
Description: eruption of a “belt” of maculopapular lesions with erythematous base along a single dermatome on the trunk
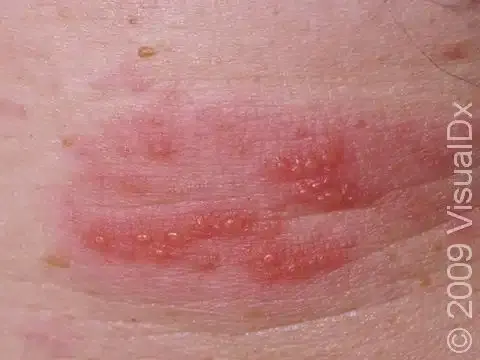







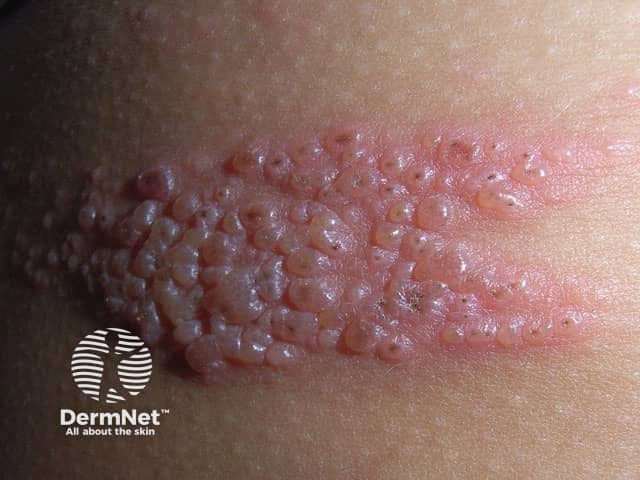

















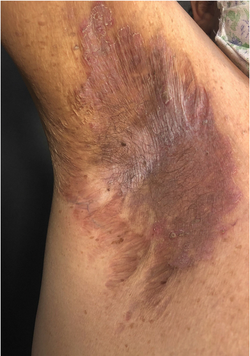
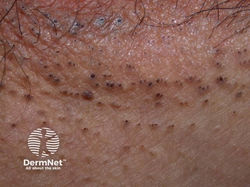
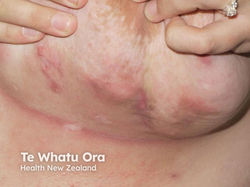
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) / Acne Inversa
Etiology: occlusion + rupture of follicles in folliculopilosebaceous units
Locations: axillae, groin, perineum, perianal, inframammary
At risk: puberty, women, obesity, cigarette smoking, IBD
Appearance: erythematous nodules, pustules, bridging comedones
Sx: recurrent tender nodules + abscesses that drain + scar
Tx:
-
mild = Hibiclens (1 min soak + then wash), Doxy, Clinda lotion, spironolactone
-
severe/scarring = biologic (Bimzelx, Humira)
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |