top of page
A
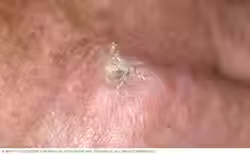
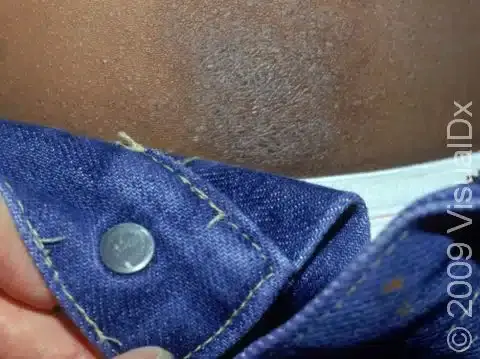
Accessory Tragus
Define: common, benign, congenital anomaly of the ear
Appearance: small, skin-colored nodule
Location: anterior to tragus
Tx: excise
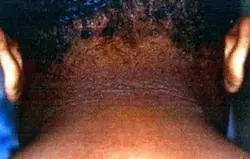
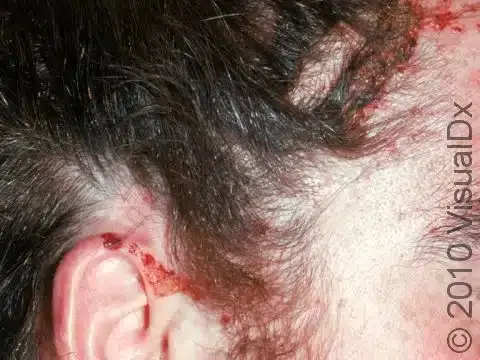
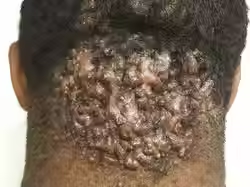
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
Etiology: short hair cuts, friction from headgear or collars
Appearance: flesh colored, dome shaped papules + pustules
Sx: itchy
Location: posterior scalp + neck
At risk: African-Caribbean descent with dark curly hair
Tx: change hairstyle, reduce friction, mild to moderate steroids with topical retinoids, oral doxy
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |
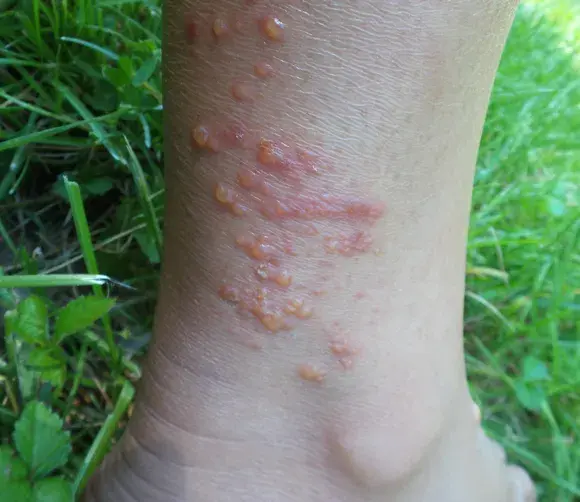
Acne Vulgaris
Etiology: folliculosebaceous unit is blocked, swollen, ruptures, and inflames the surrounding skin
Location: face, chest, upper back
At risk: oily skin, teenagers
Tx: tretinoin, adapalene, doxy, spironolactone, OCPs, isotretinoin
Types:
-
comedones: open and closed
-
papules
-
pustules
-
nodules
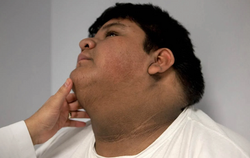
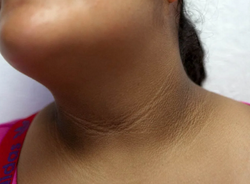
Acrochordons / Skin tags
Etiology: excess friction, insulin intolerance
Appearance: skin colored pedunculated, fleshy papules
Location: high friction areas like under breast, neck, axillae, groin
Associated with: obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, acromegaly
Tx: snipping, LN, ED
African Trypanosomiasis
Etiology: T.b. rhodensiense, T.b. gambiense
Appearance:
- At site of Tsetse fly bite, chancre forms with enlarged lymph nodes
- 2-3 weeks later, a central necrotic eschar forms
- 6-8 weeks later, trypanids form (red patches, urticaria, targetoid lesions)
Tx: before the meningoencephalitic phase = suramin; meningoencephalitic phase = melarsoprol




1/3
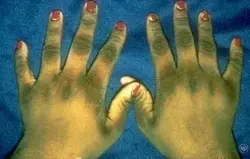
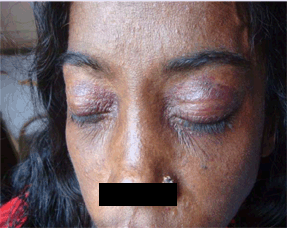
AL Amyloidosis
Etiology: accumulation of an immunoglobulin light chain (lambda > kappa) protein
Appearance: waxy skin with periorbital purpura (ex: Raccoon eyes)
Tx: high dose plasma cell directed chemotherapy with melphalan and dexamethasone
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |
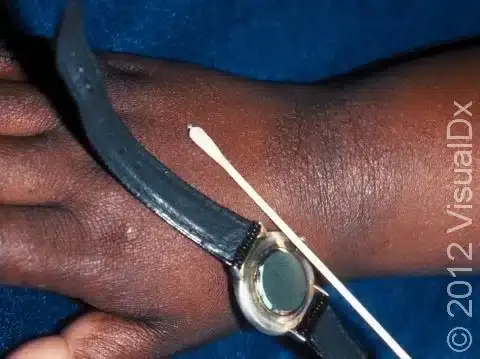
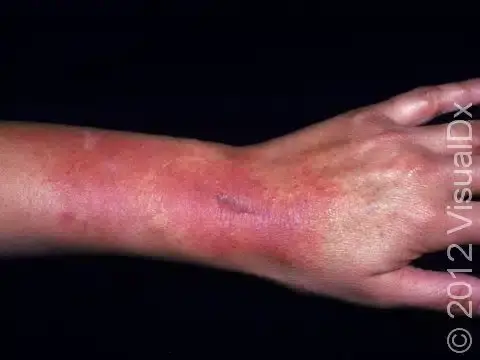
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Etiology: type IV hypersensitivity reaction to allergen (nickel, poison ivy, PCN, detergents)
Appearance: erythematous vesicular rash with edema
Tx: find causative agent and avoid, emollients and topical steroids
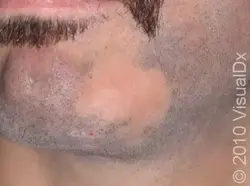
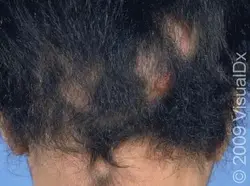
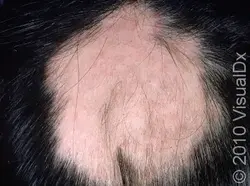
Alopecia Areata
Etiology: autoimmune condition
Appearance: hairless, smooth patches without scale, erythema, or inflammation
Test: positive hair test at periphery
Ass. conditions: autoimmune disorders, Down syndrome, atopy
Dermoscopy: exclamation point hairs
Tx: topical clobetasol solution, minoxidil, intralesional triamcinolone
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
Angioedema
Etiology: increase in local capillary permeability, usually mediated by mast cells, histamine, or bradykinin release
Appearance: swelling of dermis and SQ tissue
Location: eyes, lips, genitals
At risk: pts with chronic urticaria
Sx: painful or burning, but not pruritic
Tx: antihistamines for mild acute cases, oral prednisone for more severe cases, TXA or omalizumab for refractory recurrent angioedema
Angiosarcoma
Etiology: 20% have history of radiation to head or neck
Appearance: blue or purple macular, sometimes raised or nodular; often become ulcerated or hemorrhagic
Location: face + scalp
Tx: complete resection with wide margins
Prog: 5 yr survival is ~35%
Angular Cheilitis
Etiology: most commonly occurs due to prolonged exposure of the corners of the mouth to saliva and its digestive enzymes
Appearance: erythematous fissuring, thin scales and crust
Location: corner of mouth
At risk: pts with poor health
Ass. conditions: iron deficiency anemia, vitamin B deficiencies, protein malnutrition, chronic inflammatory diseases (IBD, Crohn Disease, Sjogren Syndrome)
Tx: most cases resolve by itself, improve hydration, lip emollients




1/8
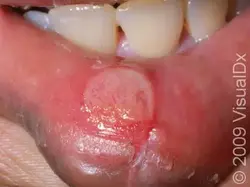
Aphthous Ulcer / Canker Sore
Etiology: unknown antigen stimulates keratinocytes via increase pro-inflammatory cytokines
Triggers: emotional stress, lack of sleep, mechanical trauma, nutritional deficiency, viral infections, certain foods or toothpastes
Appearance: round to oval ulcer with peripheral rim of erythema + yellowish adherent exudate centrally
Location: mucosa of lips, oral mucosa, tongue margins
Tx: heals spontaneously, avoid triggers
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |
Arterial Ulcer
Etiology: peripheral artery disease (atherosclerotic stenosis)
Appearance: well defined punched out ulcer
At risk: pts that smoke, have DM, high BP, high cholesterol, RF, RA, obesity
Location: distal toes
Tx: lifestyle changes, wound care
Atopic Dermatitis / Eczema
Etiology: type 1 HS reaction associated with other atopic diseases; loss of function of FLG gene = mutation in filaggrin
Appearance: irregular border pink plaque with scale +/- lichenification
Location: flexural surfaces (adults) vs extensor surfaces (children)
At risk: ‘atopic tendency’ clustering with hay fever, asthma, and food allergies
Tx: avoid skin irritants, emollients, topical steroids, bleach baths, tacrolimus, Dupixent, Nemolizumab, and so much more
Prog: 20% of children with AD had persistent sx 8 years later; children who developed AD before 2 yo had a lower risk of persistent sx than those that developed AD later in life
Atopic Eruption of Pregnancy (AEP) / Prurigo of Pregnancy
Etiology: pregnancy causing cytokine imbalance
Appearance: hyper pigmented or erythematous papules that are often grouped together
Location: extensor surfaces
At risk: 2nd - 3rd trimester
Prog: no increased risk to fetus, resolve after pregnancy
Tx: topical steroids, benzoyl peroxide, emollients




1/5
bottom of page