top of page
C
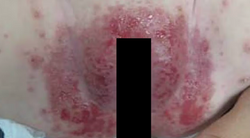
Calciphylaxis
Etiology: necrosis of skin + fatty tissue, typically in ESRD pts; can occur in those with high or normal levels of serum calcium + phosphate
At risk: females, obesity, immunosuppressed
Appearance:
- begins as surface purple retiform purpura
- then turns black in the center as a stellate shaped purpura
- then turns into dry gangrene + ulcerates
Tx: normalize calcium + phosphate levels associated with renal failure; IV infusions of sodium thiosulfate
Carbuncle
Etiology: multiple bacterial folliculitis (furuncles/boils); typically S. aureus
- mnemonic: "multiple furuncles fit in a CAR"
Appearance: erythematous pustules surrounding a hair follicle
Ass. with: Neurofibromatosis, McCune-Albright syndrome, Fanconi Anemia
Tx: antibacterial soap, oral abx
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
Carney Complex
Etiology: inactivating mutation in PRKAR1A
Inheritance: AD
Appearance: hyperpigmented macules
Location: labial, perioral, periorbital, anogenital
Ass. with: cardiac myxoma, skin myxomas, lentiginosis, pituitary adenomas, testicular tumors, primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease




1/7
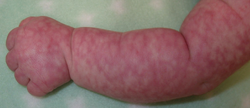
Carrión Disease (Verruga peruana / Peruvian wart)
Etiology: sandflies that carry Bartonella bacilliformis
At risk: South Americans
Appearance: eruption of red to purple nodules
Other sx: low grade fever, fatigue, headache, jaundice, pallor, HSM
Tx: abx
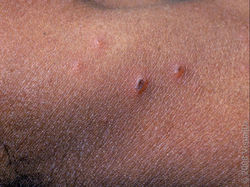
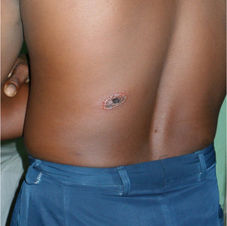
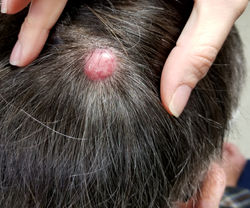
Cat Scratch Disease
Etiology: cat carrying Bartonella henselae
Appearance: erythematous papules + nodules with regional lymphadenopathy
Other sx: fever, fatigue, headache, N/V, sore throat
At risk: owning cats <12 mo old, licked/bitten/scratched by cat, immunocompromised
Tx: self limiting or azithromycin for severe/persistent sx
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |
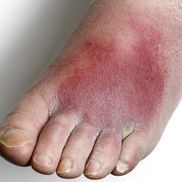
Cellulitis
Etiology: S. pyogenes, S. aureus (often from a break in skin from trauma, infix, or recent surgery)
Appearance: poorly-demarcated erythematous edematous plaque; typically unilateral
At risk: middle age + older
Location: lower extremities
Tx: oral cephalexin or IV cefazolin

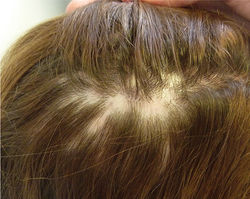
Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA)
***MC scarring hair loss
Etiology: unknown, multifactorial
At risk: African American females
Location: vertex, frontal hair line
Appearance: shiny scalp with follicular dropout
Common sx: itchy scalp, burning sensation
Tx: topical or intralesional CS, tacrolimus, Doxy
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |
Chancroid
Etiology: STI transmission of H. ducreyi
Appearance: one or more erythematous papules that quickly evolve into pustules and become larger until they break down into an ulcer
Sx: extremely painful ulcer that bleeds easily, painful swollen lymph nodes in inguinal area
Tx: azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone or erythromycin




1/4
Cherry Angioma
Etiology: aging; sometimes associated with somatic missense mutations in GNAQ and GNA11 (Q209H) genes
Appearance: erythematous to blue or purple papule or nodule
Location: trunk
Tx: ED, laser, cryo
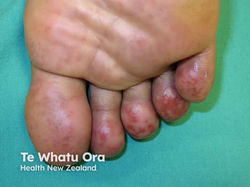
Chillblains
Etiology: tender and/or itchy bumps following exposure to damp, cold, non-freezing conditions causing constriction of small arteries and veins but a protective reflex intermittently dilates
At risk: young to middle-aged adults, females
Location: hands, feet, ears
Tx: avoid cold, wet temps, topical nitroglycerine
Prog: spontaneously regress in 1-3 weeks
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |
Chloasma / Melasma
Etiology: overproduction of melanin by melanocytes
Triggers: sun exposure, hormones, medications, ass. with family hx
Appearance: light-to-dark brown macules or patches with irregular borders
Location: bilateral cheeks
At risk: pregnancy, females
Tx: hydroquinone, tretinoin
Coccidiomycosis / Valley Fever
Etiology: allergic reaction to Coccidioides immitis
Appearance: solitary or multiple indurated papules, nodules, pustules, abscesses, ulcers, and scars
Reactive manifestation: erythema nodosum, erythema multiforme
Ass. sx: low grade fever, chills, fatigue, cough, chest pain, joint pain, lymphadenopathy
At risk: SW US, Central + South America, immunocompromised, farmers, construction workers, men
Tx: self limiting (mild), fluconazole or itraconazole (moderate), or posaconazole or ampB (severe)




1/5
Comedones: Open + Closed
Etiology: cells lining the sebaceous duct proliferate and there is increased sebum production causing debris blockage of the sebaceous duct and hair follicle
Appearance:
- open: gray, brown, black papules; keratinous contents that can be expressed
- closed: skin colored papules
Tx: benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, salicylic acid, tretinoin, adapelene

Closed comedones

Closed comedones

Closed comedones

Closed comedones

Open comedones
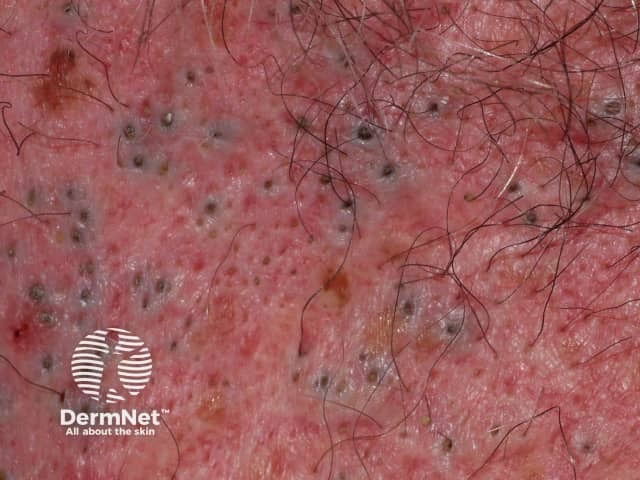
Open comedones

Open comedones
Condyloma Accuminata / Anogenital warts
Etiology: low risk HPV strains (6,11)
Appearance: soft tan-colored, cauliflower-like papules; appear 3-6 mo after infection
Location: anus or genitals
At risk: 15-30 yo, immunosuppressed
Tx: cryo, podophyllin resin, trichloroacetic acid, electrosurgery
Prevention: HPV vaccination
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
Conradi-Hünermann-Happle syndrome
Characterized by: skeletal abnormalities, skin lesions following Blaschko's lines, cataracts
Inheritance: XLD (females >)
Appearance: linear or whorled hyperkeratotic scales following the lines of Blaschko, follicular atrophoderma, pigmentary changes, and sometimes pustular lesions
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |
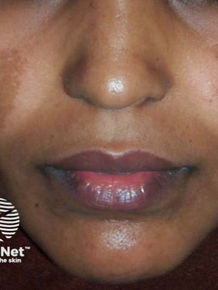
Cowden Syndrome
Etiology: LOF mutation in PTEN
Inheritance: AD
Appearance: skin colored to yellow-brown, flat topped warty papules
Ass. sx/conditions: autism, macrocephaly, thyroid goiter, breast cancer, GI polyps
Location: central face surrounding eyes, nose, mouth
Tx: 5-FU, oral retinoids












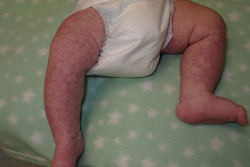
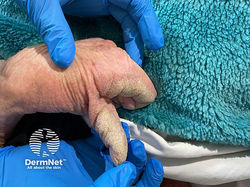
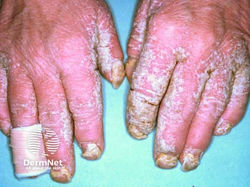
Crusted Scabies / Norwegian Scabies
Etiology: Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis
Appearance: poorly defined erythematous patches that develop into thick scaly plaques
At risk: immunocompromised, elderly, disabled or debilitated, HIV patients
Location: between the fingers, under the nails, or diffusely over palms and soles, knees, and elbows
Tx: oral ivermectin, topical insecticides
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |
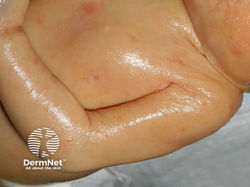
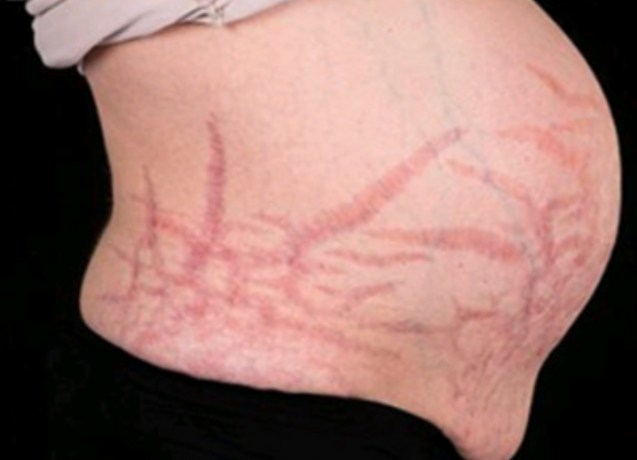
Cushing Disease
Etiology: prolonged exposure to cortisol = decreased collagen synthesis = BV rupture easier
Appearance: purple striae (stretch marks), telangectasias, acne, hirsutism
Location: abdomen
Tx: remove inciting factor for increased cortisol
Cutaneous Anthrax
Etiology: Bacillus anthracis (spores inhaled in sheep and cattle, and then humans either get inoculated with it through minor cut or inhaled or ingested spores into lung)
Appearance: papule with surrounding vesicles (develops after 1-7 days of exposure) that progress to an ulcer with black eschar and then heals into a scar within weeks
Sx: painless
At risk: farmers in Africa, Middle East, and Caribbean, workers in wool, hair, or bristle industries
Tx: doxy (for uncomplicated cases), IV or IM penicillin (for traditional cases)
Cutaneous Horn
Etiology: underlying lesions are seborrheic keratosis, viral warts (due to HPV), actinic keratosis, or well-differentiated SCC (50/50 benign vs premalignant or malignant)
Appearance: straight or curved, hard, yellow-brown projection from the skin
At risk: 60+ yo, Fitzpatrick types 1/2
Location: sun-exposed areas
Tx: excise depending on nature of lesion; always biopsy to R/O SCC
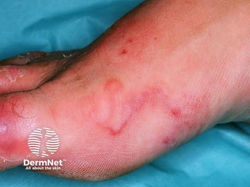
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
Etiology: A. duodenale + N. americanus
Appearance: erythematous serpiginous plaque; 2-3 mm-wide snakelike tracks stretching 3–4 cm from the penetration site
Sx: burning or tingling sensation when worm penetrates and extreme itching when worm travels
At risk: barefoot on the beach, children in sandpits, farmers
Tx: self-limiting (hookworms will die on their own in 4-8 weeks) or can prescribe thiabendazole
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |  |
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Etiology: Leishmania
Appearance: initial lesion appears 2 weeks - 2 mo after sandfly bite and is a small red papule, which gradually enlarges up to 2 cm in diameter and forms an ulcerated nodule with raised border (volcano sign)
Location: exposed skin, esp. face + extremities
At risk: living or traveling through areas where sandflies and Leishmania species are endemic (Middle East, North Africa, Asia, Central and South America)
Tx: self healing, topical non-antimonial (cryo, heat therapy, imiquimod), intralesional antimonial (sodium sibogluconate)
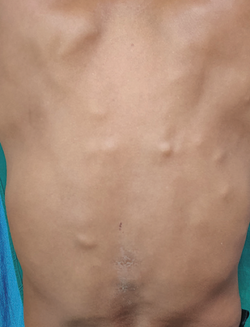
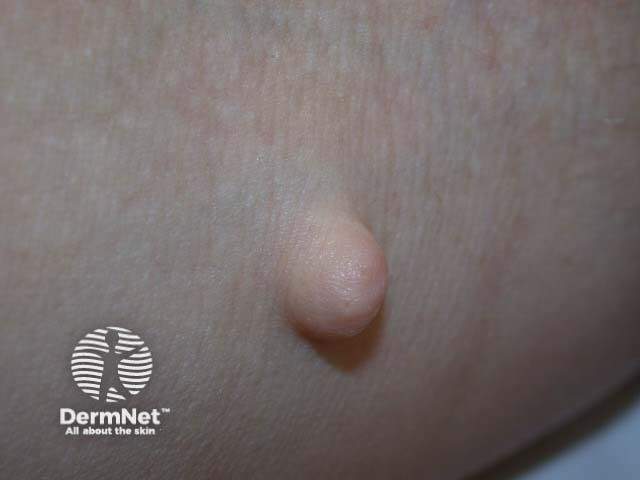
Cutaneous Neurofibroma
Etiology: unknown (solitary) or can be caused by NF1 gene mutation (multiple)
Inheritance: AD
Appearance: circumscribed, soft button-like brown, pink, or skin colored nodules with a soft or firm consistency; buttonhole sign
Location: trunk
Tx: no cure; excision for one or selumetinib may offer hope in reducing the size of plexiform neurofibromas



1/13
bottom of page