top of page
G
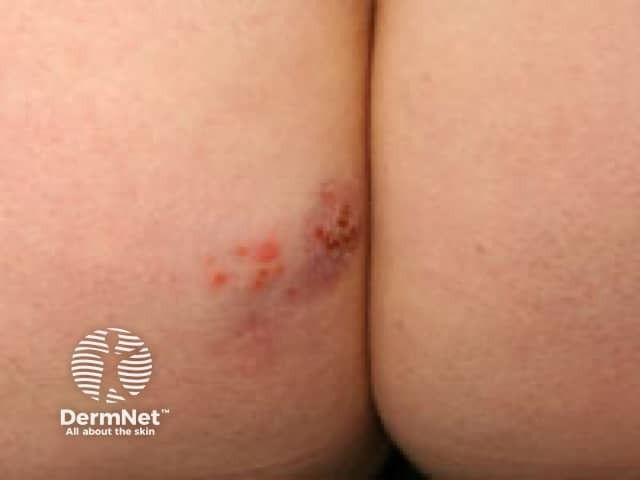
Genital Herpes
Etiology: HSV2
Appearance: vesicles sitting on erythematous base; "dew drops on a rose petal appearance"
Treatment: acyclovir



1/9
Giant cell fibroblastoma
Etiology: pediatric variant of DFSP
History: pseudo vascular spaces, hypocellular spindle cells with myxoid background
At risk: < 5 yo
Location: thigh, groin, trunk
Tx: wide excision, MOHs



1/2
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath
Location: hands, digits
Histo: multi nodule oval shaped, darker in color, giant cells ("chocolate chip cookies with extra chips and a ring of pink around it"); hyper cellular; pools of free floating mononuclear histiocytoid tumor cells that can form a halo of hemosiderin around it
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |
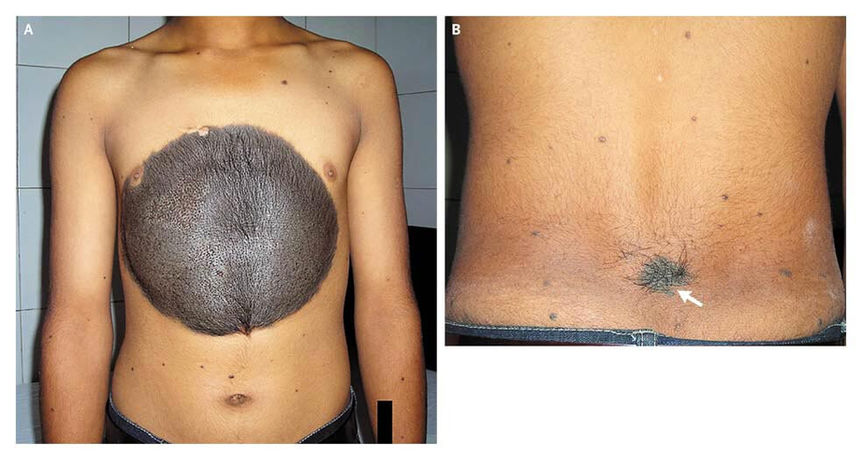
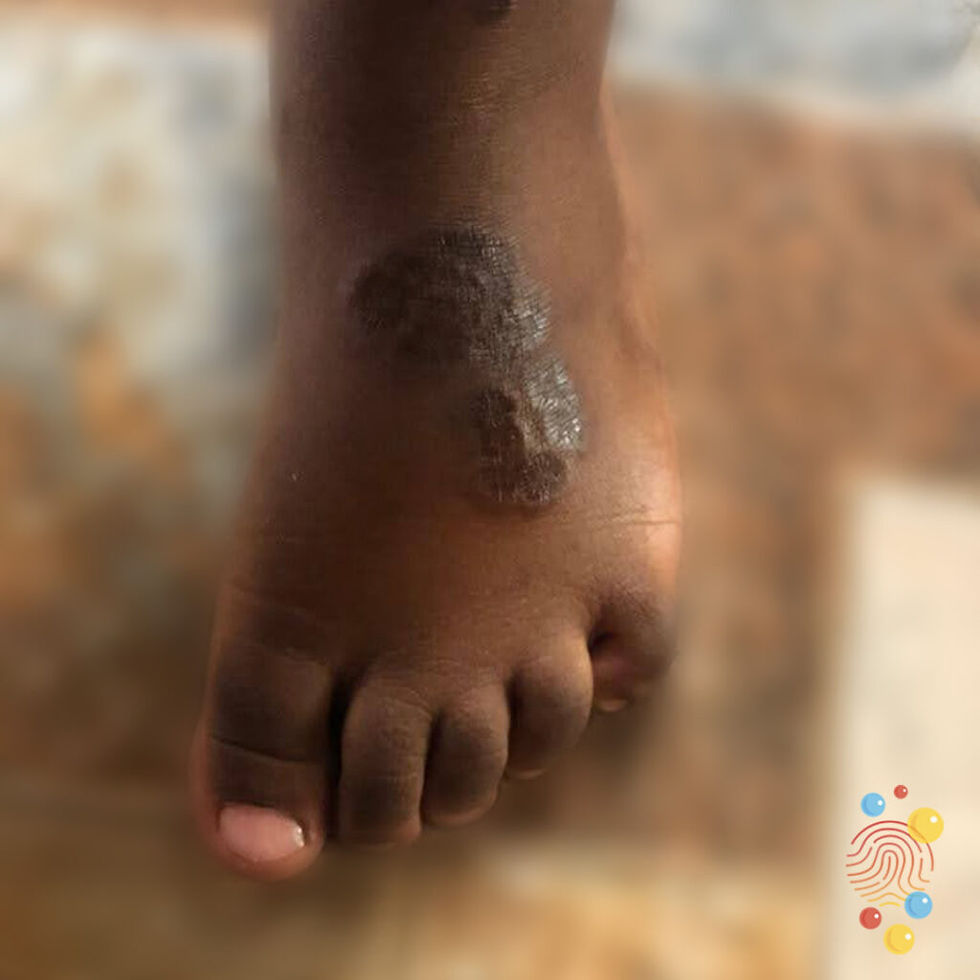
Giant Congenital Melanocytic Nevus / Bathing Trunk Nevus
Etiology: a proliferation of benign melanocytes that are present at birth or develop shortly after birth
Appearance: >20 cm
Prog: lifetime 5-10% risk of melanoma
Giant Molluscum Contagiosum
At risk: HIV, immunocompromised
Appearance: dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules with a central indentation; >10-15 mm
Location: trunk, armpits, and genital area
Tx: cryotherapy, curettage, laser therapy, topical cantharidin, tretinoin, or podophyllotoxin
Prog: Most cases resolve on their own within months to a couple of years
Gianotti-Crosti Syndrome / Infantile Papular Acrodermatitis
Etiology: reaction to a systemic viral infection (URI or GI); #1 virus = EBV
Description: papules 5–10 mm in diameter and are a deep red color
Location: develops first on the thighs and buttocks, then on the outer aspects of the arms, and finally on the face
At risk: children between the ages of 6 months and 12 years
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
Gorlin Syndrome / Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma (NBCCS)
Define: prone to developing multiple BCCs, often starting in adolescence or early adulthood
Inheritance: AD
Appearance: flesh-colored or reddish-brown spots to pearly or shiny bumps
Etiology: AD mutation to patched (PTCH) gene C9q
Description: skin tags + skin cysts (blue nevi) on face + body with multiple basal cell carcinomas
 multiple BCCs |  multiple BCCs |
|---|---|
 pits over soles | 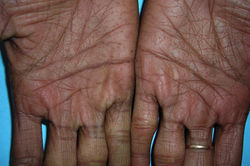 palmar pits |
 palmar pits |  multiple BCCs and scars |
 palmar pits |
Granuloma Annularae
Appearance: violasceous annular plaque with scale
Sx: itchy
Histo: surrounded by lots of mucin
Vs. tinea (no scale)
Tx: Rinvoq, UVB, Niacinamide, Zoryve
Granuloma Inguinale / Donovanosis
Etiology: Klebsiella granulomatis
Description: nodules that appear on genitalia or inguinal area that are painless, raised, beefy red, moist, smooth, and foul-smelling




1/3
Granulomatosis Infantiseptica
Etiology: Listeria monocytogenes in neonates
Description: pyogenic granulomas distributed over the whole body



1/2
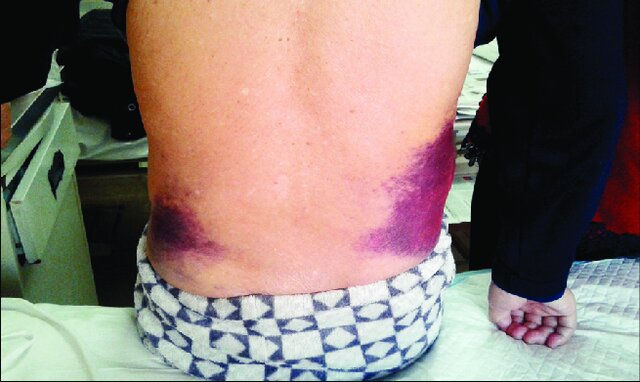
Grey-Turner sign
Etiology: retroperitoneal bleeding (kidney laceration)
Description: ecchymosis on flanks



1/3
bottom of page