S
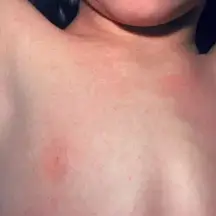
Salmon patch / Nevus simplex
Etiology: vasomotor immaturity
Appearance: pink to red blanchable patches
Location: nape of neck, eyelids, glabella
Tx: none
Prog: fades within first 2 yrs of life










Scabies
Etiology: Sarcoptes scabiei
Appearance: scattered pink papules, burrows, vesicles, and excoriations
At risk: living in close quarters (dorms, nursing homes, homeless)
Location: web spaces of fingers, umbilicus, belt line, groin, axillae
Tx: 2 doses of permethrin given 10 days apart or with oral ivermectin




Scalded Skin Syndrome
Etiology: S. Aureus (exfoliative toxin)
Description: red rash with wrinkled tissue or paper-like consistency that typically starts on the face and flexural regions, then spreads rapidly to other parts of the body; bullae can form post-rash and easily rupture causing sloughing of the skin in large sheets
At risk: <5 yo, RF immunosuppressed, DM
Location: skin folds and then disseminates in 48 hrs
Tx: burn unit/ICU, IV abx
Scarlet fever / Second Disease
Etiology: S. pyogenes (exotoxins A, B, C)
Description: fine blanching rash post sore throat; “goose skin or sandpaper like”

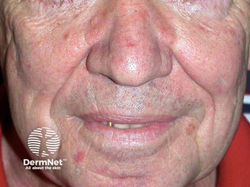
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Appearance: erythematous patches with overlying scale; greasy yellow plaque with scale
Location: scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, nasolabial folds, external auditory canal, central chest
Tx: ketoconazole twice daily, desonide cream twice daily for 1-2 weeks, antidandruff shampoo
Etiology: increased activity of sebaceous glands due to presence of Malassezia
Description: erythematous, well-demarcated plaques with greasy yellow scales in areas rich in sebaceous glands; worsens in winter and early spring; in darker skin, the plaques and scales can make the skin appear lighter
Location: scalp, face, periocular
Associated with: Parkinson’s Disease, HIV
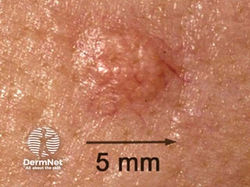
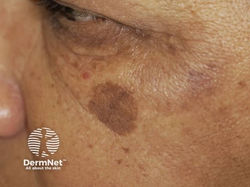
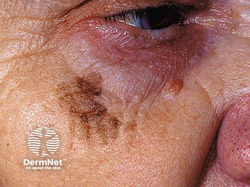
Seborrheic Keratosis (SK)
Etiology: mutations in FGFR3 genes
At risk: > 30 yo
Appearance: "stuck on" appearing warty plaque or patches
Dermoscopy: moth eaten borders, keratin pseudocysts
Tx: cryo (light skin), EDC (darker skin)
Senile Purpura
Etiology: steroids, blood thinners, poor nutritional status, fair skin, age
Location: dorsal hands, forearms
Tx: none




Sézary Syndrome
Etiology: unknown
Description:
-
Lighter skin = diffuse red rash with pruritis and edema covering >80% of body.
-
Darker skin = gray, purple or brown.
-
Early symptoms of rash appears like eczema or psoriasis
At risk: elderly




Sjögren-Larsson syndrome
Define: rare genetic disorder characterized by ichthyosis (scaly skin), intellectual disability, and spasticity
Etiology: deficiency in fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase (FALDH), which is encoded by the ALDH3A2 gene
Inheritance: AR
Tx: leukotriene B4
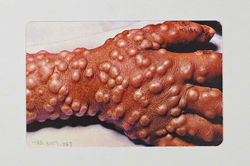
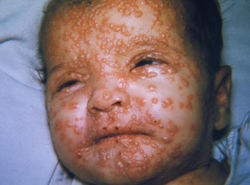
Smallpox
Etiology: smallpox virus
Description:
-
after 2-4 days of fever, body aches and headache, a rash develops
-
rash becomes raised bumps that then become fluid-filled with a depression in the center (umbilicated)
-
bumps turn into pustules that are raised, round and firm to touch
-
after about 5 days pustules begin to form a crust and then scab
-
scabs fall off leaving marks on the skin that eventually become pitted scars
Location: Rash spreads to face, arms, legs, hands and feet and to all parts of the body within 24 hours
 |  |
|---|---|
 |
Solar Elastosis / Actinic Elastosis
Etiology: chronic sun damage + smoking
Description: dry, thick, and yellow skin, with bumps, wrinkles, or furrowing
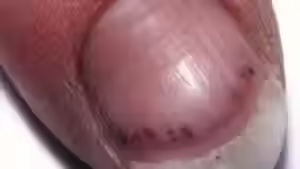
Splinter hemorrhages
Etiology: S. aureus (mostly), S. viridans (anything that can increase IC deposition)
Description: linear hemorrhage lesions
Location: nail bed



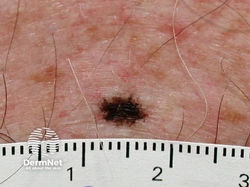
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Etiology: UV exposure over a lifetime
Location: lower legs (women), chest/back (men)
At risk: Fitzpatrick types I + II, smoking, arsenic exposure, immunosuppression, scars, tanning bed use, HPV infection
Appearance: firm, skin to pink colored, infiltrative papule or plaque that is sometimes ulcerated or covered in crust
Dermoscopy: focal scale, glomerular vessels, pinpoint hemorrhages, central keratin mass, hairpin vessels
Tx: excision, Mohs, radiation or cryo in select cases
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
Sx: fever, HA, rhinitis, and myalgias precede mucocutaneous lesions by 1-3 days; eruption initially symmetric and pain is a prominent symptom
Appearance: erythematous irregularly shaped, dusky red to purpuric macules with dark center which progressively coalesce; + Nikolsky sign
-
SJS <10%
-
TEN >30%
Tx: stop drug, go to a burn unit, IVIG, IV CS
Etiology: type IV HS drug reaction
Description: circular non-pruritic rash that is darker in the middle and lighter on the border; progresses to blisters and sores which are painful and easily peel
Location: usually starts on the upper body before quickly spreading to the face, arms, legs, genitals + mucosal surfaces
Strawberry / Infantile Hemangioma
Etiology: expresses higher levels of vasculogenic factors than normal tissue (VEGF)
Appearance: well-defined bordered erythematous papules or nodules
At risk: before 4 weeks of age
Location: head + neck
Tx: most are self resolving; if it is high risk (airway, liver, GI involvement, periorbital, PHACE syndrome, rapidly growing) then oral propranolol
Prog: involution typically begins between 6-12 mo of age
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |
Sweet Syndrome / Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
Appearance: sudden onset of painful, red or purple, “JUICY”, raised lesions (plaques, papules, or nodules)
Sx: fever
Ass. conditions: infections, IBD, + hematologic malignancies
Tx: pred
Description: erythematous, edematous, well-demarcated, tender plaques that are asymmetrically distributed
Location: face, neck, + upper extremities
Associated with: IBD and AML (20-50%)
Histo: lots of neutrophils




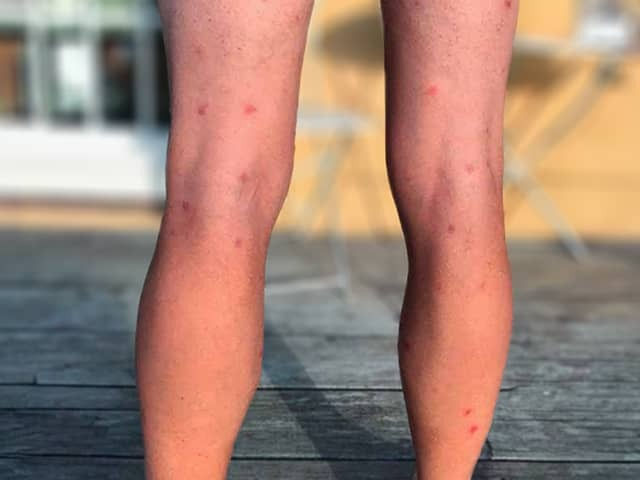
Swimmer’s Itch / Cercarial Dermatitis
Etiology: Schistosoma mansoni
Description:
-
occurs within hours of exposure after the film of water has dried on the skin
-
itch or a tingling sensation which settles quickly, leaving tiny red spots where skin penetration by the cercariae/larvae
-
Intense itch develops over hours and the red spots can enlarge to form papules and hives
-
Blisters may develop over the next 24 to 48 hours
At risk: anyone swimming in waters with infested snails











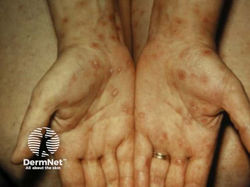
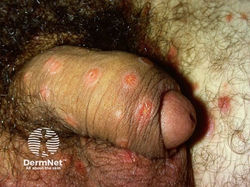
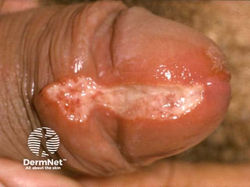
Syphilis
Etiology: Treponema pallidum pallidum
Appearance:
-
primary = chancre (firm, painless, oozes fluid)
-
secondary = maculopapular rash including palms + soles; condylomata lata (smooth, painless, warlike white lesions on genitals)
-
tertiary = gumma
Tx: penicillin
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Etiology: systemic autoimmune condition
Types/Appearance:
-
Acute cutaneous LE: butterfly/malar rash that spares nasolabial folds
-
Subacute cutaneous LE: annular scaly erythematous macules + plaques on head + extremities
-
DLE: pink infiltrative scaly patches + plaques that heal with atrophy, depigmentation, scarring
Tx: antimalarials, CS, immunosuppressants, dapsone
Systemic Scleroderma (SSc)
Etiology: autoimmune condition with noninflammatory vasculopathy and collagen deposition with fibrosis (anti-Scl-70 Ab, anti-RNA polymerase III Ab, anti-centromere Ab)
Description:
-
Limited SSc = only involving fingers and face = calcinosis cutis, Raynaud phenomenon, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia
-
Diffuse SSc = widespread skin thickening, shiny appearance, feeling of tightness + visceral involvement; sometimes have a “salt and pepper” appearance on darker skin
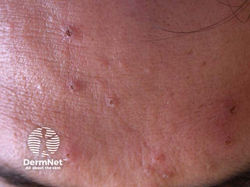
Syringoma
Define: benign skin growths that originate from sweat ducts
Appearance: small, skin-colored or yellowish bumps
Location: clustered around the eyes, but can also occur on neck, chest, abdomen, and genitals
Etiology: overgrowth of eccrine sweat glands
Description: firm bump that resembles a pimple (papule) on your skin that usually forms in small clusters or groups on your skin
Location: face (lower eyelid + upper cheeks)
Ass. with: Down syndrome