top of page
B
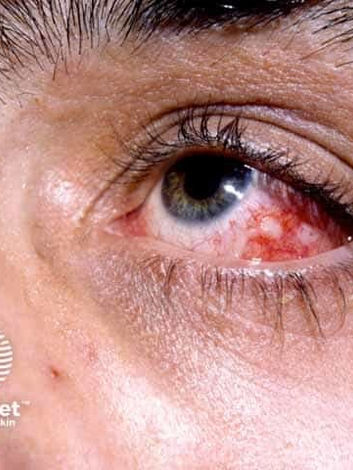
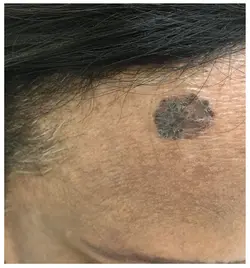
Bacillary Angiomatosis
Etiology: Bartonella henselae or Bartonella quintana + CD4 < 100; transmitted by cats or lice
Appearance: erythematous to violaceous papules that grow into nodules; very friable and bleeds profusely
At risk: HIV, immunosuppressed, organ transplant recipients
Tx: erythromycin or doxy
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
 |
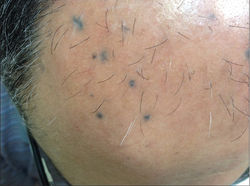
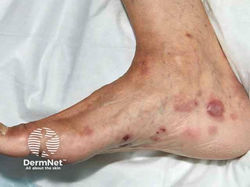
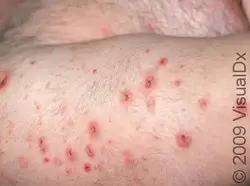
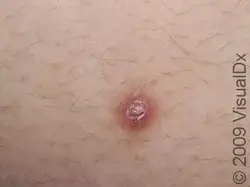
Bacterial Folliculitis
Etiology: S. aureus, unless it is Gram negative (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella or Proteus species) or Hot tub Folliculitis (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
Appearance: follicular pustules, erythematous nodules
Tx: warm compress, anti-inflammatories, mupirocin
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Behçet Disease
Etiology: unknown, assumed to be connected to autoimmune response; associated with HLA-B51
Appearance: oral + genital ulcers that are 3-5 mm, round to oval ulcers with peripheral rim of erythema + yellowish adherent exudate centrally (indistinguishable from aphthous ulcers)
At risk: eastern and central Asian, Mediterranean; 30-40 yo
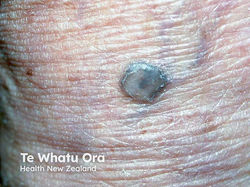
Blastomycosis
Etiology: inhale spores of Blastomyces dermatitidis (found in wood and soil, on dogs)
Appearance: purplish-gray verrucous lesions with heaped borders or friable lesions that ulcerate
Other sx: flu-like sx, productive cough
Location: face, neck, extremities
At risk: south/central and mid-western America, immunocompromised, HIV
Tx: itraconazole,amp B for severe disease




1/5
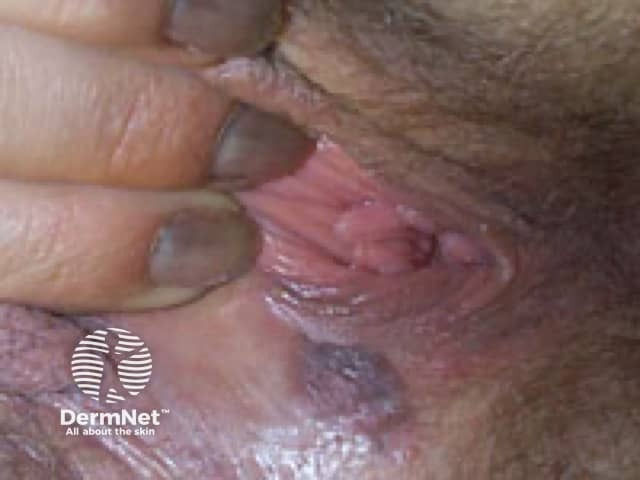
Bowenoid papulosis
Etiology: HPV 16,18
Appearance: reddish-brown papules
Location: anogenital region
Tx: monitor, ED, laser, cryo



1/3
Bullous Diabeticorum
Etiology: diabetes
Location: lower extremities
Tx: self resolving




1/4
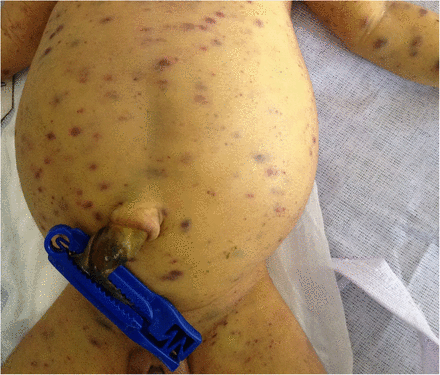
Bullous Impetigo
Etiology: S. aureus (exfoliative toxins A + B which targets desmoglein 1)
Appearance: thin roofed bullae that tend to rupture spontaneously and ooze leaving a yellow crusty rim
At risk: <2 yo
Location: face, trunk, extremities, buttocks, perineal regions
Tx: oral flucloxacillin
Burns
Etiology: any external heat/radiation source
Types:
- Superficial burn = localized, dry, blanching redness with no blisters
- Superficial partial-thickness burn = blisters, blanches with pressure, swollen, warm
- Deep partial-thickness burn = blisters that are easily unroofed, does not blanch with pressure and painful only to deep pressure
- Full-thickness burn = white, waxy, dry, inelastic, leathery, does not blanch with pressure, painless
- Deeper injury burn = white, dry, inelastic, does not blanch with pressure, painless
bottom of page