top of page
F
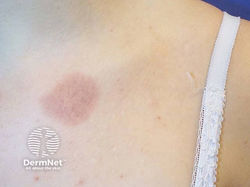
Fixed Drug Eruption
Etiology: drugs (antimicrobials and NSAIDs are most common); delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction
Appearance:
- Early lesions: sharply demarcated erythematous macules
- Late lesions: round or oval plaques that may evolve to become bullae and then erosions (occur 30 - 8 hours after ingesting drug)
Location: mouth, genitalia, face, hands, feet
Prog: resolve days to weeks after drug is discontinued; PIH may persist
Tx: discontinue suspected medication, topical or systemic CS
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
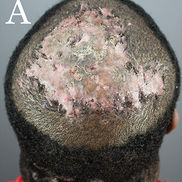
Folliculitis Decalvans
Etiology: considered to be the result of an abnormal immune response to S. aureus, although this is not yet proven
Appearance: erythematous, swollen, and scaly patches and plaque with crust and pustules (like CCCA, but smaller and with pustules)
Sx: itching, pain, and burning sensation
Tx: clindamycin, CCS (topical + oral or injected)

Focal Dermal Hypoplasia / Goltz Syndrome
Etiology: rare genetic disorder affecting tissues derived from ectoderm and mesoderm
Inheritance: XLD
Location: mouth, genitals, anus
Ass. conditions: coloboma, missing or webbed fingers, hypoplastic teeth, low set ears, cleft lip or palate, bladder exstrophy, kidney abnormalities, CHD, vision and hearing impairment
Appearance: thin or absent skin areas, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, and fat herniation; following Blaschko's lines; wart-like growth
Tx: vascular lasers for cutaneous papillomas and telangectatic areas
Frey's Syndrome
Etiology: postoperative complication involving parasympathetic fibers regenerating on sympathetic fibers of sweat glands (auriculotemporal branch of V3 is cut during an excision of the parotid gland and reinnervates the skin sweat glands in front of the ear)
Appearance: redness + sweating
Location: preauricular
Triggers: post-eating, thinking or dreaming about food
Tx: symptom control, botox, aluminum antiperspirant, oral or topical glycopyrrolate



1/2
bottom of page